Finally, a new version (4.0.0) of the app is available (see Download). Since last year, a lot of features has been added (see here for all of them). First, the Windmeter, the cheaper anemometer (~60$) from WeatherFlow may now record air speed. It doesn't record temperature, humidity and pressure as the WeatherMeter device though (~90$). Second, the BlueFly vario may also be connected (some personal notes about it here): the interest for CdaCrr is mainly, for the moment, to provide a very precise barometer (+/-10cm) to compare for instance virtual elevations and real ones to validate the Cda and Crr estimations or to detect some oddities. So, currently, the app may records data from 5 sensors (power, speed, heart rate, air speed, barometer) and sometimes the app suffers unhappily from disconnections between the phone and its sensors. At last, the app is based more and more on BLE protocol (device detection has been improved, see there) and ANT+ will be less and less supported.
Tuesday, December 28, 2021
Sunday, October 31, 2021
Racing with an aero system
The legality of using aero sensors when racing is unclear. Nevermind, I recorded data during two training out and backs, and the time trial itself:
Monday, April 12, 2021
Monday, April 5, 2021
Thursday, December 31, 2020
Wednesday, December 30, 2020
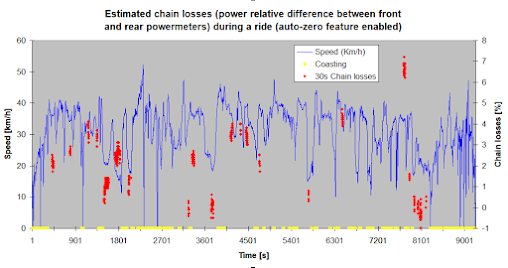
Chain losses
It seems that the lower the speed, the lower the chain losses. The auto-zero feature of my G3 has a flaw which explains the variations (0-7%). But there is one moment (near 1 hour) where no coasting happened and chain losses decreased from 2% (@40km/h) to 0% (@20km/h).
Monday, December 28, 2020
Live CdA
Lot of data to monitor today: instantaneous wind, estimated chain loss (30s average) and real time CdA (~60s average, +/-0.005 precision). Fun to play with the last feature to set a low mark at 0.285. Again seen some oddities to food the geek mind during this cold ride.
Sunday, November 8, 2020
Monday, June 15, 2020
Sunday, June 7, 2020
Elevation profiles
Ok, up to now, it is the best measured elevation (normalized at 0 for start/end of the lap) profile I get for my virtual wind tunnel venue. I rode slowly (18-20 km/h) on the 3420m of the venue and recorded data with the Joule 2.0 computer which had a great resolution (0.1m). The elevation is normalized in order to have H(0)=H(L)=0m.
Update 2020/07/15:
Added data during a ride (30-32 km/h) from the Blue Fly Vario variometer (named here BFV) built on a MS5611 barometer inside (providing same 0.1m resolution for elevation). Profiles are very closed, but we can notice that during the ride at higher speed with the BFV, the barometer reported lower altitude at some points (eg: 750-1200m), but not everywhere (eg: 250-500m).
Update 2020/07/15:
Added data during a ride (30-32 km/h) from the Blue Fly Vario variometer (named here BFV) built on a MS5611 barometer inside (providing same 0.1m resolution for elevation). Profiles are very closed, but we can notice that during the ride at higher speed with the BFV, the barometer reported lower altitude at some points (eg: 750-1200m), but not everywhere (eg: 250-500m).
Friday, October 11, 2019
Saturday, December 22, 2018
Test of the dynamic calibration of the airspeed device
Bad and good news from the velodrome test today. I implemented recently in the app, a dynamic procedure for calculating the correction factor to be applied to the raw air velocity measured by the anemometer. This factor is calculated at each lap. The anemometer (blue) was placed on the left drop of the bike during the test:
Several turns are made where I changed the position of my hands (hoods then drops, again hoods). Thus, we can see that when the left hand on the hood is close to the anemometer (certainly creating a local air acceleration), the calibration factor decreases by about 2% (1.095 to 1.075), and so a similar erreor increase of ~4% on the calculated CdA:
The good new is that if we keep a same position, the factor is well
calculated with acceptable variability +/- 0.5%. We can also assume that
by placing the bike's anemometer in another location, the issue may be reduced.
Sunday, August 12, 2018
Power meter data quality
Yesterday, for the first direct comparison during a turbo session, I got results, which confirmed my suspicions, between my two current powermeters, a Power2max NG-Eco (2 months old) and a PowerTap G3 (recently changed). Unfortunatly, I deleted some of the data. Today, during a ride with intervals of several minutes, I recorded the following averages:
One (or the two?) gave an unexplicated difference during the first lap of the two runs (the relative difference does not depend of the gear ratio and is constant at +/-0.5% during the whole lap). Auto-zero feature was activated on the two power-meters and I stopped pedalling during the laps. I have some guesses about the suspect. More to come.
Tuesday, January 2, 2018
Cheapest Android phone to use CdaCrr bike computer
The app is currently tested with the following phones:
- Blackview A7
- Samsung J5, S4 mini, S4, S5
- Xiaomi Redmi Note 7
- Wiko Pulp 4G
* You would need also a powermeter (~450$), a speed sensor (~35$), and a phone mount on your bike (~10$). You would also highly benefit from the Weatherflow anemometer (~70$) if you are seriously hooked to field testing.
Sunday, December 3, 2017
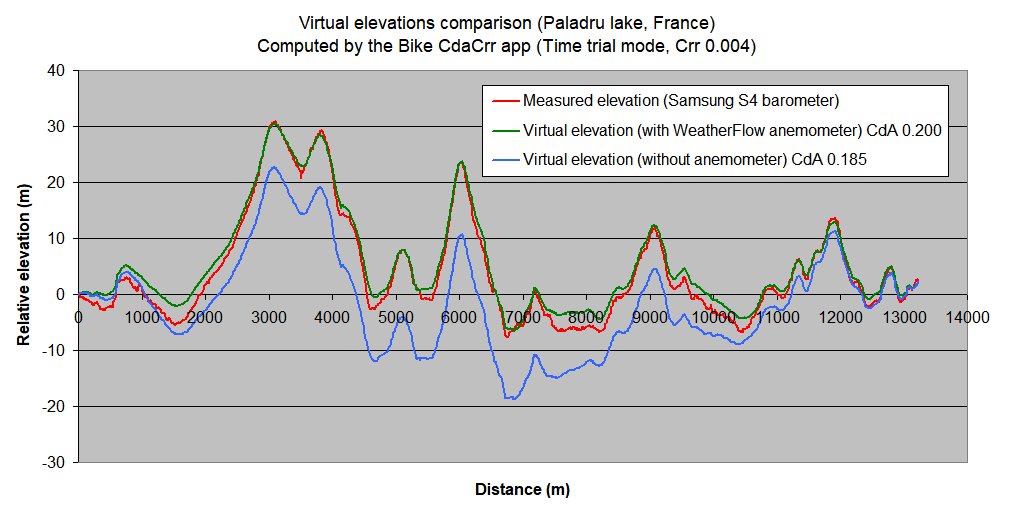
Virtual elevations
Monday, August 7, 2017
Track model
According to Google Maps, the 250 meters track has straight of length 74.8 meters and turn radius of 16.0 meters.
The measured incline along the black line in the turns is ~30°, for 6° in the straights.
The measured incline along the black line in the turns is ~30°, for 6° in the straights.
Friday, March 17, 2017
Velodrome session with high wind
Back to the outdoor velodrome. I wanted to see if the anemometer could improve precision with high wind conditions. The results, after three runs of 10 laps (trying to keep the same relaxed position on the hoods of my road bike) are:
We can notice that the wind, measured near the ground (the anemometer was mounted on the drops), is in the 5-15 km/h range (weather station indicated 22 km/h this day).
Quick updated conclusions for the moment:
- with low and constant wind conditions (0-5 km/h), data anemometer is useless as the effect is nearly cancelled (CV~1-2%)
- with higher wind conditions (>5 km/h), anemometer is mandatory to maintain acceptable precision (CV~1.5-3%) whereas for apparent CdA (wind data is not included into the model) variability is way of.
- variability from run to run is still an issue in my protocol (0.343, 0.353, 0.342) even if it should be lower with the use of a time trial bike.
Saturday, January 21, 2017
Sunday, January 15, 2017
Outdoor velodrome with an anemometer
On an outdoor velodrome (250m length), the rider selected the "Defined lap length" mode in the app and did a first run of 28 laps, then a second run of 22 laps. The Weather Meter anemometer, which is mounted on the front of his TT bike, records axial apparent speed:
We clearly see that the wind, during the session, is not constant at all, and has a range of [1-5] km/h. The mean axial wind, on the whole session, is -0.19 km/h. It indicates that the calibration factor used in the app to take in account the stagnation effects seems slightly underestimated. It is confirmed by the computation of real CdA vs apparent CdA (air vs bike speed in the drag force):
First run:
0.303 +/-0.006 (CV: 1.8%)
0.301 +/-0.005 (CV: 1.8%)Second run:
0.308 +/-0.003 (CV: 0.9%)
0.304 +/-0.005 (CV: 1.7%)
The apparent CdA is lower than the real CdA during the two runs, which is unexpected. Nevertheless, even if there is a biais on the real CdA, we can notice two things:
-Variability is low for the real CdA, which is a very good point for the validation of the anemometer
-During out and back ride or velodrome testing, apparent CdA is accurate enough when wind is low (less than 5 km/h) as the effect is nearly cancelled in the drag force
Tuesday, November 22, 2016
Ride with an anemometer
A friend is currently testing intensively the CdaCrr app with the Weather Meter anemometer mounted on the bike. The air speed is now recorded every second, so the rider average CdA is more accurately computed.
On the smartphone screen, two figures now appear on the top left, with first the real CdA (wind is used in the model), and the apparent CdA (model with no wind). The two are of interest, with the first one you can see the influence of your position changes during the ride, even with unsteady wind. By the second value, we can learn how drafting is important during a group ride, or how tail or headwind affects quantitatively the air resistance measured by the apparent CdA figure.
 |
| 2 hours ride. Segments where CdA is averaged are indicated by the red marks. |
During his last ride (between 11am and 1pm), the nearest airport station has reported a wind speed of 14.8 km/h and an east direction (so between ~80 and 100 degrees from the north). Meteorological station are at a standard height of 10 meters, so wind speed should be translated to a value near the ground (there is a velocity profile created by shear) with the Hellman estimation. A rule of thumb is to divide the value by two (or even three, according to this post). So, we guess a wind speed near the ground of 5-8 km/h.
CdaCrr app has recorded the following data: axial wind speed (subtracted bike sensor speed from anemometer air speed) and direction of travel (given by the phone GPS):
We can notice the sinusoidal tendency of axial wind speed with direction. Indeed, the axial wind speed seen by the rider is given by:
AxialWindSpeed = WindSpeed * cos(BikeDirection-WindDirection)
By fitting the data with a sinusoidal function (red curve below), we find out the prevailing wind direction 84°, east as indicated by the weather station.
The fit also gives us the sinusoidal amplitude, WindSpeed in the previous formula, as 3.9 km/h with a wind in the previous graph between -10 and 10 km/h. Compared to the 5-8 km/h of the meteorological station, there is no surprise here.
The idea of using GPS data to check wind direction was read in this great article.
The idea of using GPS data to check wind direction was read in this great article.
Monday, April 25, 2016
Monitoring apparent CdA during a race
Monday, February 1, 2016
Velodrome test
Field testing isn't easy.
Lesson one: one turn (250 meters) per lap is enough to compute a CdA value. Adding more turns for a lap do not reduce variability.
Lesson two: the first turns should be systematically discarded.
Lesson three: keeping a constant position on the bike should be the goal number one.
Friday, January 22, 2016
1.0 Release
The CdaCrr app has been released this week on the Google Store.
For the moment, it has only been tested on Samsung S4/S5 and Sony Xperia Active phones and it records correctly from a PowerTap powermeter.
It implements Virtual Elevation method (aka: Chung method) to measure CdA (aerodynamic coefficient of drag) and Crr (rolling resistance coefficient) when riding a bike.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)